Greenhouse thermos: how it is arranged and how to make it yourself?
Anyone who has his own site would like to receive fresh vegetables not only seasonally, but year-round. In addition, in the autumn-winter period, the cost of fresh vegetables is quite high, so their implementation will bring additional profit. Unfortunately, not a single crop can grow in an ordinary greenhouse in winter, since the ground temperature on the surface is too low. To the aid can come a special design called "greenhouse thermos".
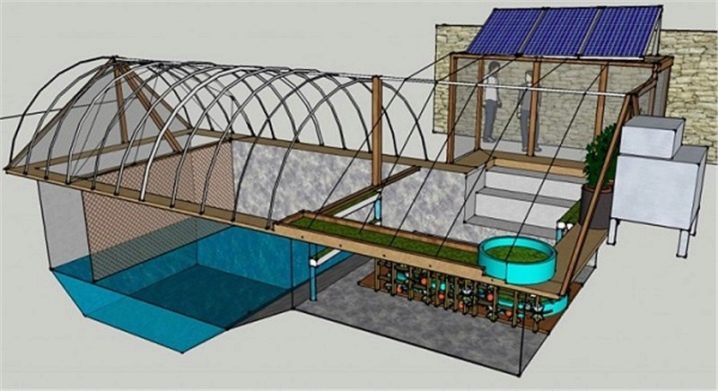
For the first time this design was proposed for growing plants in conditions of severe frost. Such a thermos is a high greenhouse, most of which is located below the ground. Today it is the warmest and most profitable greenhouse for obtaining not only seasonal crops, but also a good harvest of citrus, which rarely bear fruit in the middle lane.
Advantages and disadvantages
Greenhouses of the new model are significantly different from traditional greenhouses with electric heating.
Its benefits include the following.
- Reliability and durability. More durable materials are most often used to install the structure than for small greenhouses, so it will last more than ten years.
- High light transmittance. It is about 91% and an order of magnitude higher than that of the old options. Plants will receive a maximum of sunlight and will quickly develop and grow.
- Weather protection. Such greenhouses can be safely installed in areas with hurricane winds and frequent hail. Its foundation and frame are almost completely dug into the ground, so it is protected from damage.
- Well keeps heat inside due to tightness. The best coating according to numerous reviews of the owners is polycarbonate. Even in the absence of heating inside the greenhouse in a thirty-degree frost, it maintains a positive temperature inside it. This will help save additional funds that are spent on the installation and use of additional heaters.
- The microclimate in the underground greenhouse is as close as possible to the natural one, which affects the growth rate of vegetables and the number of their fruits.
If during the construction all technologies are followed and high-quality materials are chosen, then a warm construction will be able to survive without major repairs for about 15 years.
From the minuses of such a greenhouse, the following can be noted.
- The complexity of installation. It is quite difficult to independently design and install all the systems of such a greenhouse. It is necessary to have an idea about the installation not only of the frame, but also of electrical wiring and ventilation system. In addition, it is necessary to build a small sewer system.
- The building, though it quickly pays off, requires very significant one-time costs. You need to buy expensive materials and pay for the work of builders.
If it is possible to build the structure independently, it will significantly reduce the financial burden. At the same time, the cost of self-maintenance of the structure is practically absent. In addition, such a greenhouse allows you to reduce the amount of chemicals that protect plants from various pests, as in the winter they simply have nowhere to take.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of such an energy-saving greenhouse is that the ground at a depth of 2-3 meters not only does not freeze through, but practically does not change its temperature depending on the air temperature. Minor fluctuations are more dependent on the depth of the groundwater, and not on frost or snow. The difference in night and day temperatures does not exceed 5 degrees, so gardening is possible throughout the year. The skeleton of the structure can be made of either traditional metal or wood, or in the form of brickwork or concrete blocks.
The upper part of the greenhouse, protruding above the ground, is transparent. Through it penetrate the sun's rays, which are so necessary for the growth of fruits and vegetables. The roof can be convex or flat, be made of glass or polycarbonate. Sometimes the roof can be like the unique Scandinavian geothermals, which transmit 4 times more sunlight than the usual “houses”. Such a greenhouse is called "vegetarian", there is even enough light in the twilight for the growth and development of plants. The internal walls of the building, located underground, are covered with a special mirror material.Light, penetrating through the roof, is reflected from the shiny surface and scatters inside such a greenhouse. In this way, plants receive several times more light than under natural conditions.
Kinds
Despite the same principles of work, greenhouses, thermoses can be divided into several separate types.
Underground
On the surface of the earth only the roof of such a greenhouse is visible, and the rest of the space is dug into the ground. In order to make it easy to descend, it is necessary to erect a small ladder near the entrance. Particular attention is paid to such a greenhouse lighting. Since the light penetrates only into the upper transparent “window”, it is necessary either to arrange additional artificial lighting or to cover the walls with reflective material. The roof can be made in the same design as the Scandinavian vegetarian. So the loss of sunlight will be minimized. Such greenhouses can be up to 6 meters deep and are used for growing southern crops even in the winter period of the middle climatic zone.
Recessed
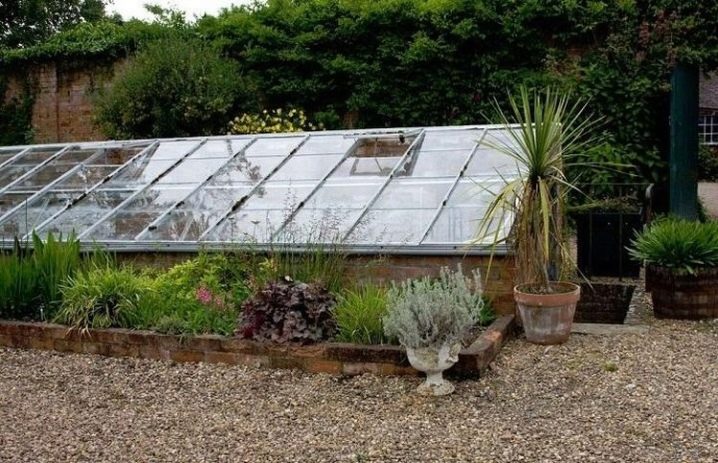
Most often you can find just such a variant of the greenhouse-thermos, since it is only slightly inferior to the underground greenhouse, but much easier to install.A greenhouse is a small dugout, whose walls are recessed into the ground at a certain height. Part of the walls and the roof of the greenhouse remain above the ground and are made of transparent glass or polycarbonate. There is much more light in such a greenhouse, so it is enough to sheathe the inner surface with a mirror material, and artificial lighting will not be needed.
Chinese
Unlike traditional domestic buildings, such a greenhouse has only one transparent wall. The remaining walls are built from brick, concrete, wood or from the earth. The frame of some greenhouses is a large arc, resting directly on the wall of a residential building. Such a greenhouse is usually not too deep, as a sufficient amount of heat comes from the living space for normal plant growth.
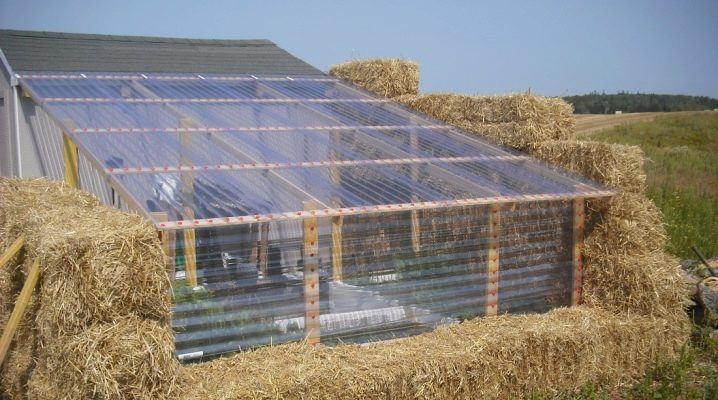
Polycarbonate overhead
Polycarbonate protects plants from precipitation and strong winds quite well. The design is stable and it is easy to replace a separate element in it without dismantling the entire structure. However, in the winter in the above-ground greenhouse it is cold enough, the soil on the surface may be completely frozen, therefore it is necessary to install additional heating and a complicated ventilation system.
In order to determine the type of thermos greenhouse, you must select the place on which it will be built. First of all, it is necessary to analyze the soil so that the structure does not “float” on the foundation of groundwater.
The strength of the structure and the size of the recess for a greenhouse are selected based on how deep the soil freezes through the winter and to what point the air temperature in each specific region falls.
How to do?
Before proceeding with the purchase of necessary materials, it is necessary to draw up a drawing of the future pit greenhouse. With it, it will be easy to calculate the right amount of materials, as well as calculate all quantities. If the greenhouse will be located on a slope, it is necessary to calculate the correct angle of inclination of the roof to get the maximum amount of natural sunlight. The most optimal angle is from 35 to 45 degrees.
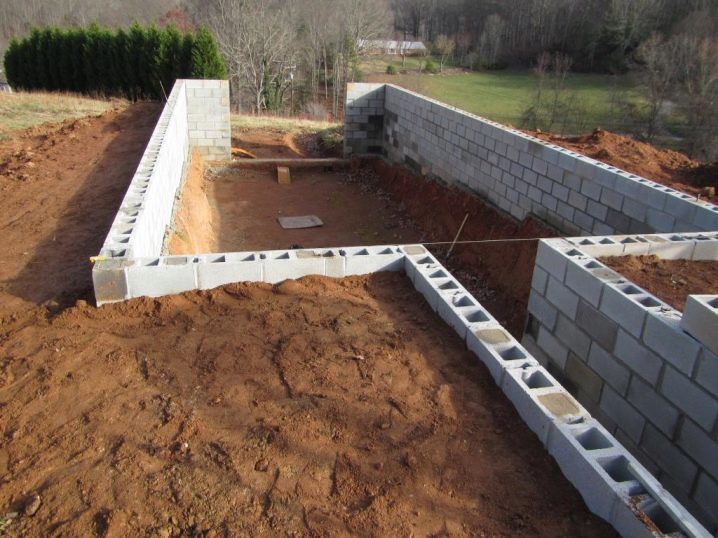
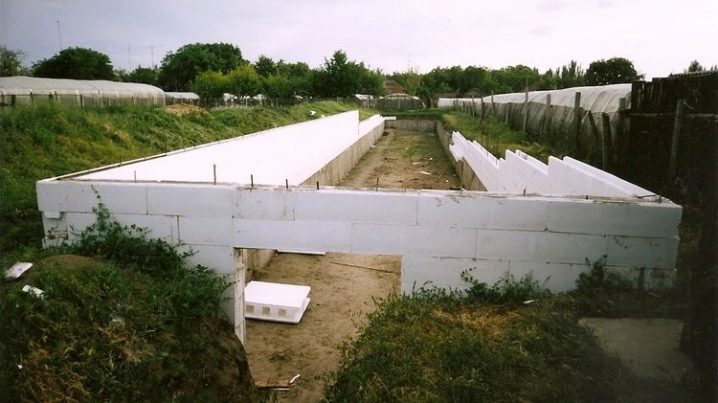
For the construction of underground walls are best suited thermoblocks, which are made of two polystyrene plates, connected by bridges. They are installed as a permanent formwork, and the top is poured with concrete.Expanded polystyrene will allow to retain a greater amount of heat inside the room than the usual monolith of concrete.
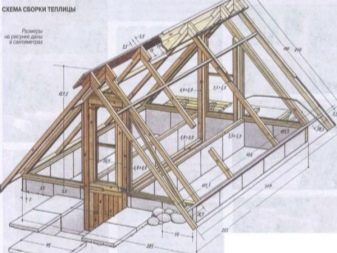
For the roof frame, you will need a wooden beam or a more expensive but stronger metal profile. It is best to order a frame made of metal profiles from professionals, since to work with it you will need your own welding machine and considerable skill to work with it. Wood must be pre-treated with special protective impregnations that protect it from moisture and pests.
To cover the roof, you can use a dense plastic film, glass or polycarbonate. The film is cheaper than other materials, but its service life will be only 2-3 years. And if the film breaks through in one place, then it will have to be removed and changed completely. Glass is quite durable, but fragile and very expensive. It is best to buy plastic shock-resistant polycarbonate, which in the case of deformation can be replaced with pieces. In addition, polycarbonate protects plants from excessive ultraviolet radiation.
You will need a shovel, hammer, tape measure and level, trowel, concrete mixer and jigsaw. For mounting fasteners you will need a screwdriver or a set of screwdrivers and pliers.In addition, you need to stock up on fasteners, sand and gravel for laying the foundation, as well as plaster for the treatment of the inner surface of the walls.
After calculating and purchasing everything you need, you can proceed directly to the installation process. The construction of the pit greenhouse is done in several stages.
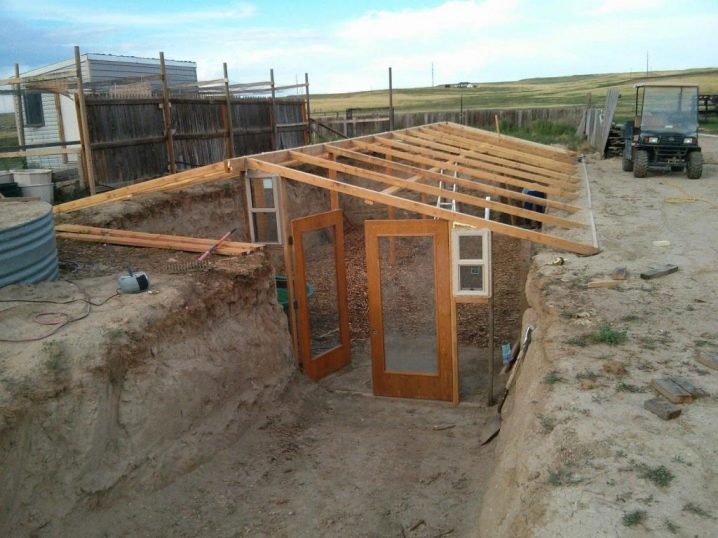
Digging the foundation pit
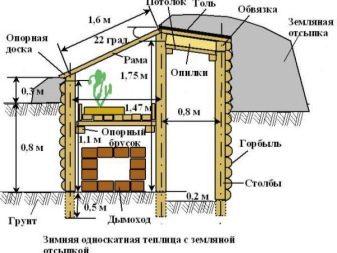
Since the main part of the greenhouse will be located underground, it is necessary to dig a deep pit for it. The greenhouse should go down at least 2 meters. All edges are neatly aligned, the foundation is poured around the perimeter. The walls and roof of the future greenhouse will rest on it.
Erection of underground walls
After the foundation hardens and hardens completely, you can start building walls. The best option would be to attach the thermal block to a metal or wooden frame. They will protect the space from temperature extremes and infiltration of wastewater.
Insulation of underground walls and space heating
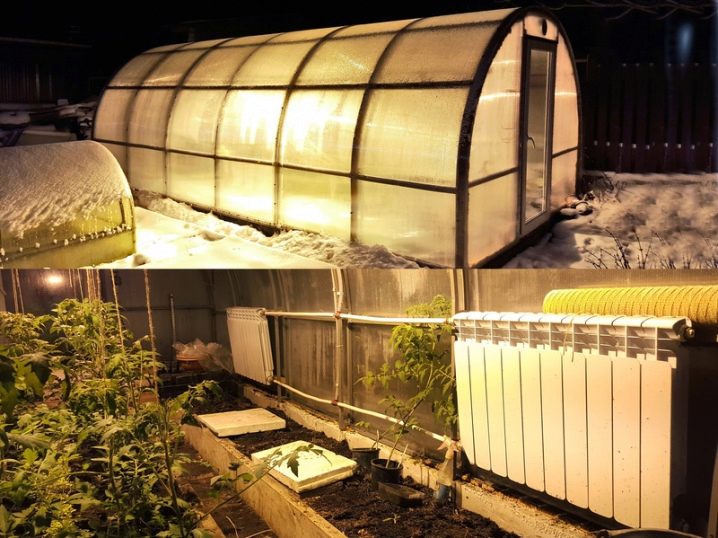
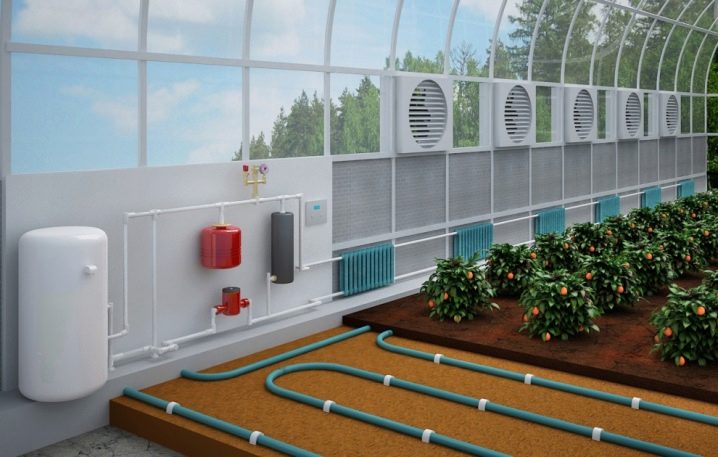
With the solution, all joints and slots between the separate blocks of the wall are carefully rubbed over. The entire inner surface is covered with a thermal insulator in the form of a special film in order to maintain the desired temperature and microclimate.If in the region in the winter there are strong frosts, from above such film can be additionally covered with foil-insulated insulation. For additional heating of the soil, it is possible to install a “warm floor” system under it. To heat the air, you can use heat accumulators in the form of barrels or large bottles filled with water.
Roof erection
The roof on a wooden frame is made with one or two ramps. The ridge connects with the walls with long rafters, on which crossbeams are installed. A film is laid on top of the frame, or polycarbonate or glass is mounted. For better thermal insulation, you can lay polycarbonate in two layers, inserting a special profile between them.
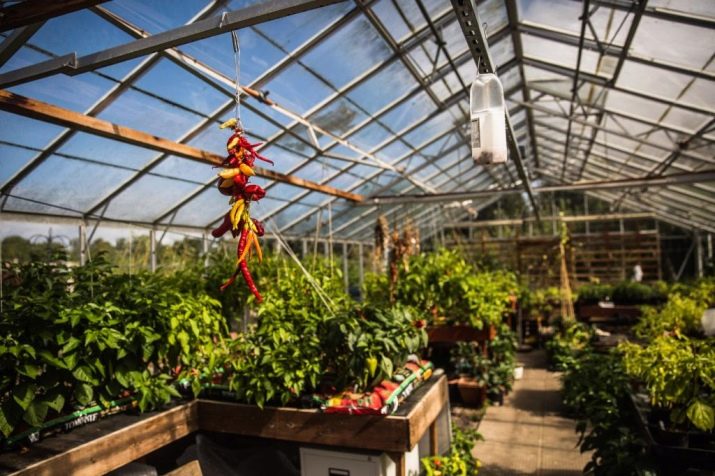
Interior arrangement
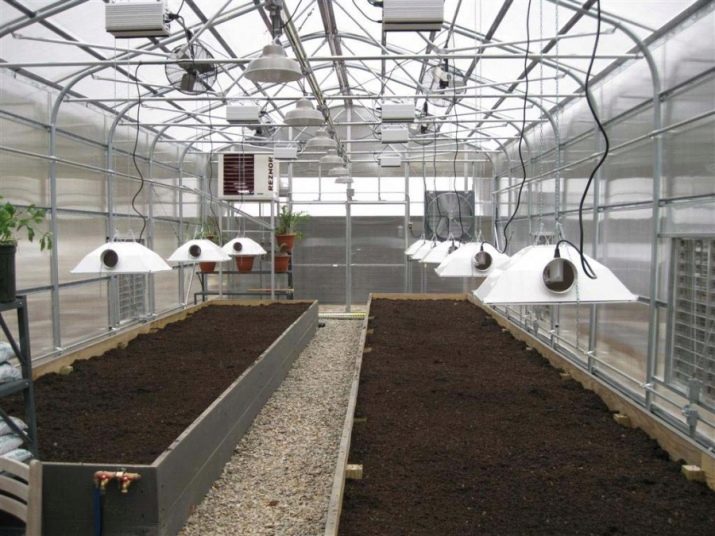
The greenhouse is electricity and plumbing, mounted sewer system, if necessary, set the automatic watering. With a lack of lighting put the lamp with which the yield will be much higher. Ground is poured on the floor of the greenhouse and beds are formed.
Lighting and arrangement of beds
For the installation of additional lighting greenhouses fit the following types of lamps.
- Fluorescent. Such lamps do not heat the air, while giving light to the plants in the desired spectrum. They are inexpensive, durable and can be mounted both on a horizontal and on a vertical surface.
- Gas discharge. These are mercury, metal halide or sodium lamps, which are most often used in large industrial greenhouses. They shine in the spectrum necessary for plants with greater light output than luminescent ones, however, their cost is much higher.
- LED. Such lamps are most often used in small home greenhouses. They have the longest service life and adapt to the desired spectrum. Depending on the needs of the culture, you can choose blue, red or combination light. The only disadvantage of such equipment is its high cost.
In addition to proper lighting in the greenhouse thermos, you need to take care of the organization of the correct beds. They should be about 100-120 cm wide and about 5-10 cm tall. A large width of the beds is inconvenient to maintain, and a smaller one is too small for the normal development of the root system of many vegetables. Between the beds must be at least 50 cm of free space for tracks.If the greenhouse is wide enough for three ridges, then the central one can be made up to 150 cm wide, since it can be processed from two sides. Each bed must be installed on-board limiters from the side of the tracks. From abundant watering on them a lot of water flows, and the boards with a height of 7-10 cm will protect the tracks from erosion. With the correct depth of the greenhouse-thermos and well-equipped lighting it will be possible to harvest several times a year. The main thing is to fertilize the soil in time and observe the compatibility of different crops.
All the advantages of the underground greenhouse thermos are detailed in the video below.