Types, composition and use of sulphate-resistant cements
Very few people doubt the strength and durability of reinforced concrete structures, but still it is worth noting that under the influence of external environmental factors the material tends to collapse rather quickly. The main causes of concrete destruction are wind, groundwater, sunlight, frequent rain and cold. That is why the use of new technologies in the production of building mixtures is so important.
Specialized sulphate-resistant concrete comes to the aid in the fight against the destruction of concrete structures.
Special features
Sulfate-resistant cement is made on the basis of fine grinding of Portland cement clinker mixed with gypsum, a special case of ordinary Portland cement with a feature in the form of increased resistance to the effects of sulfates.
Special requirements are placed on the quality of the clinker used in the manufacture of sulphate-resistant cement. So, its chemical composition is strictly standardized:
- the concentration of tricalcium silicate is not more than 50%;
- aluminate concentration - not more than 5%;
- alumina module - must be more than 0.7%;
- the combined content of C3A + C4AF is less than 22%.
Such restrictions are introduced to protect the resulting structure from sulphate corrosion.
Using
The use of sulphate-resistant cements is justified for the construction of structures subject to aggressive environmental influences.
Namely:
- severe frosts and temperature drops;
- frequent precipitation and changes in humidity, flooding, ebbs and flows, flood, groundwater;
- the movement of the ground, its subsidence or, conversely, swelling;
- exposure to aggressive chemical fluids, for example, groundwater with unstable composition;
- seismic activity.
Therefore, most often the scope of application of sulphate-resistant cements is:
- zinc sulphate bridge piles;
- hydrotechnical constructions working with sea or ocean water;
- underwater and underground arrays;
- sea and river piers;
- reinforced concrete structures;
- structures with increased tension.
Varieties of sulphate-resistant cement
Consider the main types of sulfate-resistant cement, depending on the composition:
- Portland cement without additives. The introduction of mineral and inert additives in this type of cement is unacceptable. It is a versatile material, resistant to temperature and humidity.
- Slac Portland cement. The main additive is granulated blast furnace slag, it is ground together with clinker and makes up 40–60% of the total volume of the mixture. Slag used as an additive must meet the standard for the presence of aluminum oxide in it - no more than 10-12%. The weak point of slag Portland cement is the instability to freeze.
- Portland cement with the addition of mineral additives. As mineral additives, slag in the amount of 15-20% of the total volume, pozzolan, a combination of pozzolan or microsilica with slag can be used. Mineral supplements usually make up 5-10%. This type of sulphate-resistant cement has excellent resistance to freezing and moisture changes.
- Pozzolanic portland cement. Contains a mixture of blast furnace slag and pozzolans. Pozzolans are active mineral additives of volcanic origin, such as, for example, ash or pumice.Unlike Portland cement, it is more resistant to sulphate corrosion, but at the same time it tolerates sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
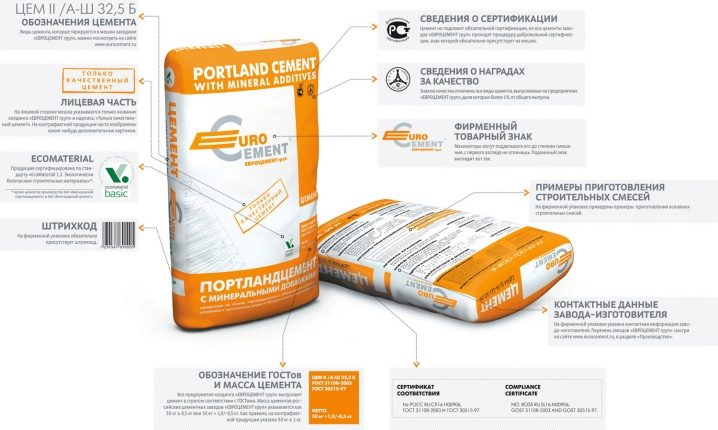
Sulphate-resistant cement marking
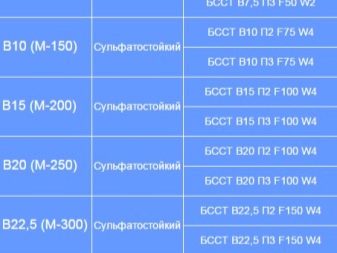
When purchasing sulphate-resistant cement, attention should be paid to labeling on the packaging. It means maximum compressive strength. The main common brands are M300, M400, M500. Accordingly, the strength of these cements will be from 300 to 500 kg / cm² (or from 30 to 50 MPa).
It must be remembered that during long-term storage, the strength of the composition may decrease, for example, in 3 months it may decrease by up to 10%.
Cement reaches its maximum compressive strength at 28 days after pouring.
- Sulfate-resistant slag Portland cement is of all available markings - M300, M400 and M500.
- Portland cement with the addition of mineral additives is marked - M400 and M500.
- Portland cement without additives is labeled - M400.
- Pozzolanic is labeled - M300 and M400.
Properties of sulphate-resistant cements
Sulfate-resistant cements are quick-drying.
- Setting time - from 45 minutes to 10 hours.
- Water demand 22-28%. This is an important characteristic that is used to properly dilute the initial mixture with water in order to obtain a solution of the desired consistency.
- Grinding fineness. For cements with a content of mineral additives of sedimentary origin, the residue on the sieve with cells of 80 microns is not more than 15%
Color and white portland cement
Aggressive environmental conditions are no reason to forget about the aesthetic appearance of the structure. White Portland cements are particularly prevalent; their manufacturing mechanism is very similar to ordinary cement, with the exception of the use of white clinker.
An important point in the production of white clinker is the use of carbonate rocks and clays with a very low concentration of iron and manganese oxides. To enhance the whiteness of the clinker, it is whitened using chemical reduction of iron carbide 3 to iron oxide Fe3O4.
In white Portland cement, its whiteness is especially appreciated, for example, there are 3 degrees of whiteness of cement, which differ in the degree of light reflection.
Color Portland cement is also produced on this basis. It is easy to make from white clinker in a mixture with coloring substances. Iron hematite ore (for obtaining red and brown hues), phthalocyanine pigments (for obtaining green and blue), iron oxide pigment (yellow), and soot for obtaining gray and black hues are most often used for coloring.
Recommendations
It is worth noting that sulphate-resistant cements are an important part in the construction of structures subjected to severe climatic conditions, such as changeable humidity and temperature fluctuations.
It is necessary to take due responsibility to the choice of materials, because for different conditions sulphate-resistant cements are selected individually.
In most cases, an important selection criterion is the type of soil, its acidity and density. But it is also worth when choosing to pay attention to the fact that the purchased products meet state quality standards (GOST).
How to choose cement, see the next video.